Analyze split screen
This article based on
AOSP9.0.
Split screen is my best favorite multi-window feature when I use Android phone. This article will analyze its logic show how this awesome feature is implemented.
SystemUI
The split screen’s entry is in system ui’s recents. In RecentsView, if the user select one app to start in split screen mode with ui choice, RecentsViewl.onBusEvent will try to start the task of this app to split screen mode.
RecentsView.onBusEvent
final ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptionsCompat.makeSplitScreenOptions(
dockState.createMode == SPLIT_SCREEN_CREATE_MODE_TOP_OR_LEFT);
if (ActivityManagerWrapper.getInstance().startActivityFromRecents(event.task.key.id,
options)) {
// Other code
}
The ActivityManagerWrapper.startActivityFromRecents calls ActivityManagerService.startActivityFromRecents directly.
ActivityManagerService
The ActivityManagerService.startActivityFromRecents calls ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityFromRecents directly. The starting activity from recents logic is the same as normal starting activity in most occasion. We will show the important points for recents and split screen.
Restore task from recent_tasks files
The RecentsView passes the task id of app to the ActivityManagerService, and ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityFromRecents will try to restore the task with the specified id from recent_tasks if the task with the same id doesn’t exist. The work is done by ActivityStackSupervisor.anyTaskForIdLocked:
ActivityStackSupervisor.anyTaskForIdLocked
final TaskRecord task = mRecentTasks.getTask(id);
// Other code
if (!restoreRecentTaskLocked(task, aOptions, onTop)) {
if (DEBUG_RECENTS) Slog.w(TAG_RECENTS,
"Couldn't restore task id=" + id + " found in recents");
return null;
}
RecentTasks.getTask
TaskRecord getTask(int id) {
final int recentsCount = mTasks.size();
for (int i = 0; i < recentsCount; i++) {
TaskRecord tr = mTasks.get(i);
if (tr.taskId == id) {
return tr;
}
}
return null;
}
ActivityStackSupervisor.anyTaskForIdLocked will use RecentTasks to get restored task from recent_tasks files.
RecentTasks.loadUserRecentsLocked will call TaskPersister.restoreTasksForUserLocked to restore tasks from /data/system_ce/user_id/recent_tasks/*_task.xml, and use the result to populate RecentTasks.mTasks.
Initialize launch stack
After getting restored task from recent_tasks files, ActivityStackSupervisor.anyTaskForIdLocked will call ActivityStackSupervisor.restoreRecentTaskLocked to assign launch stack for restored task.
ActivityStackSupervisor.restoreRecentTaskLocked
final ActivityStack stack = getLaunchStack(null, aOptions, task, onTop);
ActivityStackSupervisor.getLaunchStack
return display.getOrCreateStack(r, options, candidateTask, activityType, onTop);
ActivityDisplay.getOrCreateStack
<T extends ActivityStack> T getOrCreateStack(@Nullable ActivityRecord r,
@Nullable ActivityOptions options, @Nullable TaskRecord candidateTask, int activityType,
boolean onTop) {
final int windowingMode = resolveWindowingMode(r, options, candidateTask, activityType);
return getOrCreateStack(windowingMode, activityType, onTop);
}
ActivityDisplay.createStackUnchecked
return (T) new ActivityStack(
this, stackId, mSupervisor, windowingMode, activityType, onTop);
The ActivityStackSupervisor.restoreRecentTaskLocked invoking chain will call ActivityDisplay.createStackUnchecked to create an instance of ActivityStack with the stack id and windowing mode.
In ActivityStack initialization method, there is an important invoking:
ActivityStack.ActivityStack
// Other code
postAddToDisplay(display, mTmpRect2.isEmpty() ? null : mTmpRect2, onTop);
ActivityStack.postAddToDisplay
activityDisplay.addChild(this, onTop ? POSITION_TOP : POSITION_BOTTOM);
if (inSplitScreenPrimaryWindowingMode()) {
// If we created a docked stack we want to resize it so it resizes all other stacks
// in the system.
mStackSupervisor.resizeDockedStackLocked(
getOverrideBounds(), null, null, null, null, PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}
ActivityDisplay.addChild
addStackReferenceIfNeeded(stack);
ActivityDisplay.addStackReferenceIfNeeded
} else if (windowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARY) {
if (mSplitScreenPrimaryStack != null && mSplitScreenPrimaryStack != stack) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("addStackReferenceIfNeeded:"
+ " split-screen-primary" + " stack=" + mSplitScreenPrimaryStack
+ " already exist on display=" + this + " stack=" + stack);
}
mSplitScreenPrimaryStack = stack;
onSplitScreenModeActivated();
}
ActivityDisplay.onSplitScreenModeActivated
private void onSplitScreenModeActivated() {
mSupervisor.mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
try {
// Adjust the windowing mode of any affected by split-screen to split-screen secondary.
for (int i = mStacks.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
final ActivityStack otherStack = mStacks.get(i);
if (otherStack == mSplitScreenPrimaryStack
|| !otherStack.affectedBySplitScreenResize()) {
continue;
}
otherStack.setWindowingMode(WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY,
false /* animate */, false /* showRecents */,
true /* enteringSplitScreenMode */, true /* deferEnsuringVisibility */);
}
} finally {
mSupervisor.mWindowManager.continueSurfaceLayout();
}
}
The ActivityStack.postAddToDisplay will add itself to ActivityDisplay firstly, and then resize docked stack if current stack is in split screen primary windowing mode. If we select to start app in split screen mode, its windowing mode is WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARY. ActivityDisplay.addStackReferenceIfNeeded called by ActivityDisplay.addChild will active split screen mode if the added stack’s windowing mode is WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARY. ActivityDisplay.onSplitScreenModeActivated will set other stacks’ windowing mode in current display to WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY except WINDOWING_MODE_FREEFORM, WINDOWING_MODE_PINNED and other stacks don’t support split screen mode(ActivityStack.affectedBySplitScreenResize). So there is an important conclusion: when starting an app to split screen stack with windowing mode WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARY, the ActivityDisplay will set other stacks in this display to WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY except WINDOWING_MODE_FREEFORM, WINDOWING_PINNED and other stacks don’t support split screen.
The following is a screenshot after starting split screen primary:
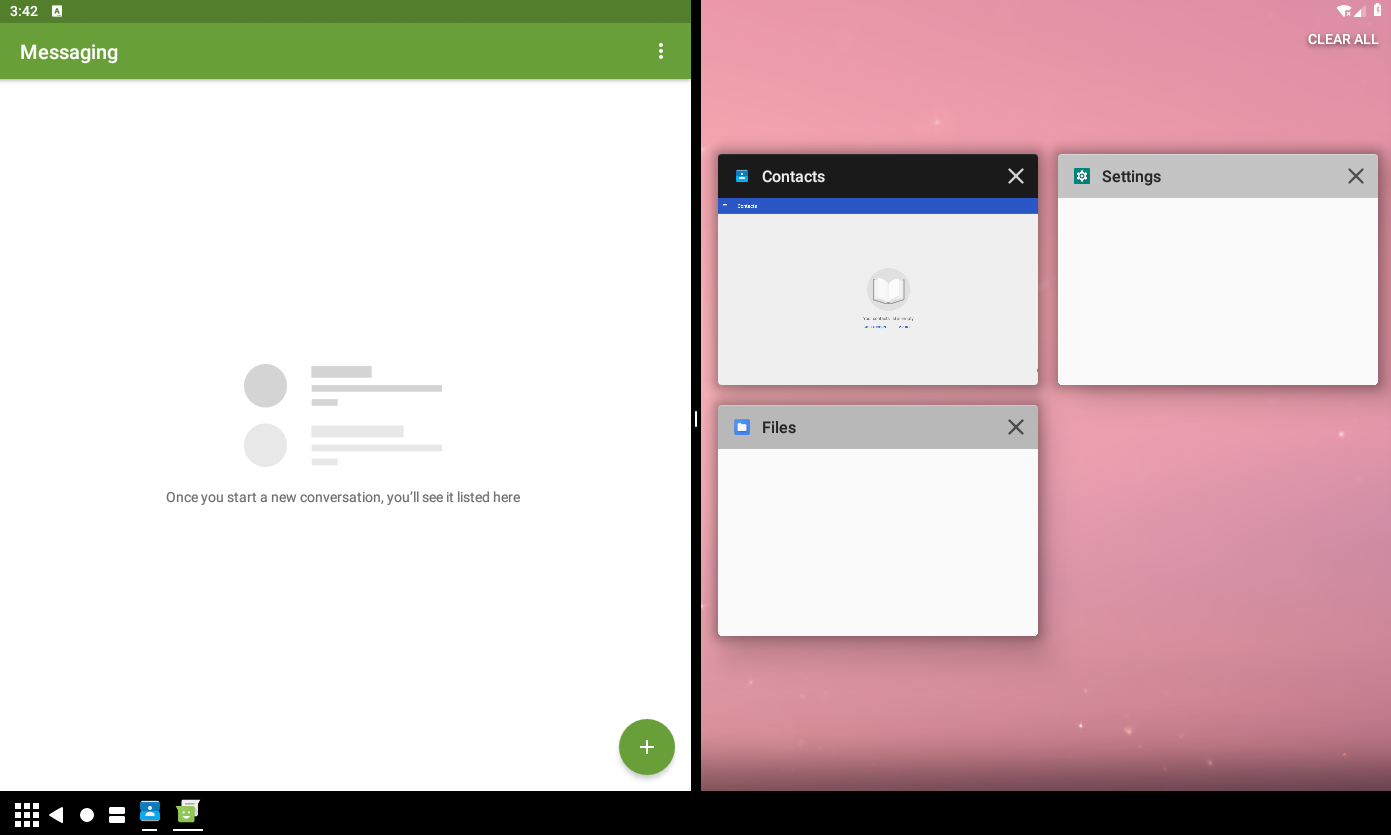
Starting split screen secondary
In above diagram, the message app is in split screen primary stack, and other apps are in split screen secondary stacks, one app has one stack, and their windowing mode is WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY. What if we start another app from recents? What if we start another fullscreen app from app drawer? They will be started to split screen secondary stack.
From the above Activity.getOrCreateStack code snippet, we can see that ActivityDisplay.getOrCreateStack will call ActivityDisplay.resolveWindowingMode with ActivityOptions to calculate the final windowing mode.
ActivityDisplay.resolveWindowingMode
final boolean inSplitScreenMode = hasSplitScreenPrimaryStack();
if (!inSplitScreenMode
&& windowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN_OR_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY) {
// Switch to fullscreen windowing mode if we are not in split-screen mode and we are
// trying to launch in split-screen secondary.
windowingMode = WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN;
} else if (inSplitScreenMode && windowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN
&& supportsSplitScreen) {
windowingMode = WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY;
}
If there is split screen primary stack, and windowing mode is WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN, the ActivityDisplay.resolveWindowingMode will change windowing mode to WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY. So there is another conclusion: the fullscreen task will be started to split screen secondary stack if there is a split screen primary stack and this task supports split screen. The app started from recents has the default windowing mode WINDOWING_MODE_UNDEFINED, and it will be translated to WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN in ActivityDisplay.resolveWindowingMode, so it will be started to split screen secondary stack. The fullscreen app started from app drawer also will be started to split screen secondary stack.
The following is a screenshot after starting another fullscreen app from recents:
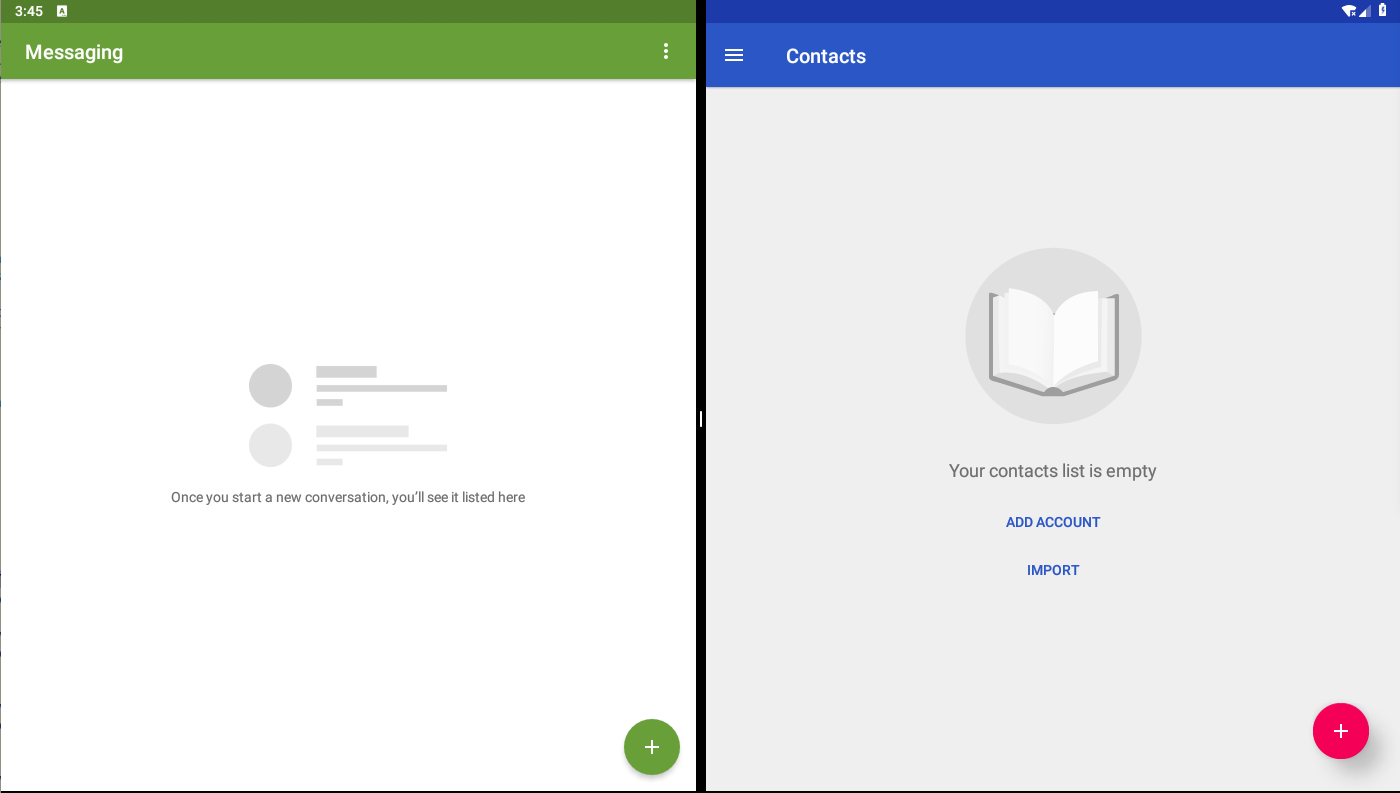
Resize docked stack
In ActivityStack.postAddToDisplay, it will resize docked stack if current stack is split screen primary stack. It will use bounds from window controller as docked stack bounds. The bounds rect is initialized by ActivityStack.createStackWindowController in ActivityStack.ActivityStack before ActivityStack.postAddToDisplay.
The process chain of creating StackWindowController will call TaskStack.onDisplayChanged to notify the display changed event:
ActivityStack.createStackWindowController->StackWindowController.StackWindowController
->DisplayContent.createStack->DisplayContent.TaskStackContainers.addStackToDisplay
->TaskStack.onDisplayChanged.
The TaskStack.onDisplayChanged will call TaskStack.getStackDockedModeBounds to calculate bounds for current windowing mode, through TaskStack.updateBoundsForWindowModeChange and TaskStack.calculateBoundsForWindowModeChange for docked stack or split screen stacks.
TaskStack.getStackDockedModeBounds
final int position = new DividerSnapAlgorithm(mService.mContext.getResources(),
di.logicalWidth,
di.logicalHeight,
dockDividerWidth,
mDisplayContent.getConfiguration().orientation == ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT,
mTmpRect2).getMiddleTarget().position;
if (dockOnTopOrLeft) {
if (splitHorizontally) {
outBounds.right = position;
} else {
outBounds.bottom = position;
}
} else {
if (splitHorizontally) {
outBounds.left = position + dockDividerWidth;
} else {
outBounds.top = position + dockDividerWidth;
}
}
The TaskStack.getStackDockedModeBounds will use DividerSnapAlgorithm to get the middle position of screen, and use it to restrict docked stack bounds based on split orientation. For example, the split screen primary stack shows in left screen of PC(width > height), will get the bounds of left half screen. Otherwise TaskStack.getStackDockedModeBounds will use following logic to calculate the bounds for split screen secondary stack:
TaskStack.getStackDockedModeBounds
if (!dockOnTopOrLeft) {
if (splitHorizontally) {
outBounds.right = dockedBounds.left - dockDividerWidth;
} else {
outBounds.bottom = dockedBounds.top - dockDividerWidth;
}
} else {
if (splitHorizontally) {
outBounds.left = dockedBounds.right + dockDividerWidth;
} else {
outBounds.top = dockedBounds.bottom + dockDividerWidth;
}
}
The above code snippet will calculate stack bounds for split screen secondary stack.
Divider
From the above two diagrams, we can see a divider between split screen primary and split screen secondary. It’s a special window with type TYPE_DOCK_DIVIDER. The DividerWindowManager.add in system ui will help to add divider window to system. The window content is DividerView in systemui. The DividerView will help to response to drag divider to change split screen size.
Layer
In DisplayContent.AboveAppWindowContainers.assignChildLayers, it will create a surface called SplitScreenDividerAnchor for divider, because divider doesn’t have AppWindowToken, and use SplitScreenDividerAnchor’s layer as the base layer of divider.
DisplayContent.AboveApWindowContainers.assignChildLayers
if (wt.windowType == TYPE_DOCK_DIVIDER) {
wt.assignRelativeLayer(t, mTaskStackContainers.getSplitScreenDividerAnchor(), 1);
continue;
}
If we execute adb shell dumpsys SurfaceFlinger when system is in split screen mode, we can see following result:
+ BufferLayer (splitScreenDividerAnchor#0)
Region TransparentRegion (this=739b84e38208 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
Region VisibleRegion (this=739b84e38010 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
Region SurfaceDamageRegion (this=739b84e38088 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
layerStack= 0, z= 8, pos=(0,0), size=(2800,2800), crop=[ 0, 0, -1, -1], finalCrop=[ 0, 0, -1, -1], isOpaque=0, invalidate=1, dataspace=Default, defaultPixelFormat=RGBx_8888, color=(0.000,0.000,0.000,1.000), flags=0x00000000, tr=[1.00, 0.00][0.00, 1.00]
parent=com.android.server.wm.DisplayContent$TaskStackContainers@e778792#0
zOrderRelativeOf=none
activeBuffer=[ 0x 0: 0,Unknown/None], queued-frames=0, mRefreshPending=0, windowType=-1, appId=-1
+ BufferLayer (WindowToken{b2619d4 android.os.BinderProxy@e697327}#0)
Region TransparentRegion (this=739b84f15208 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
Region VisibleRegion (this=739b84f15010 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
Region SurfaceDamageRegion (this=739b84f15088 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
layerStack= 0, z= 1, pos=(0,0), size=(2800,2800), crop=[ 0, 0, -1, -1], finalCrop=[ 0, 0, -1, -1], isOpaque=0, invalidate=1, dataspace=Default, defaultPixelFormat=RGBx_8888, color=(0.000,0.000,0.000,1.000), flags=0x00000000, tr=[1.00, 0.00][0.00, 1.00]
parent=mAboveAppWindowsContainers#0
zOrderRelativeOf=splitScreenDividerAnchor#0
activeBuffer=[ 0x 0: 0,Unknown/None], queued-frames=0, mRefreshPending=0, windowType=-1, appId=-1
+ BufferLayer (90fc77d DockedStackDivider#0)
Region TransparentRegion (this=739b84f18208 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
Region VisibleRegion (this=739b84f18010 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
Region SurfaceDamageRegion (this=739b84f18088 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
layerStack= 0, z= 0, pos=(676,0), size=(2800,2800), crop=[ 0, 0, -1, -1], finalCrop=[ 0, 0, -1, -1], isOpaque=0, invalidate=1, dataspace=Default, defaultPixelFormat=RGBx_8888, color=(0.000,0.000,0.000,1.000), flags=0x00000000, tr=[1.00, 0.00][0.00, 1.00]
parent=WindowToken{b2619d4 android.os.BinderProxy@e697327}#0
zOrderRelativeOf=none
activeBuffer=[ 0x 0: 0,Unknown/None], queued-frames=0, mRefreshPending=0, windowType=-1, appId=-1
+ BufferLayer (DockedStackDivider#0)
Region TransparentRegion (this=739b84edb208 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
Region VisibleRegion (this=739b84edb010 count=1)
[676, 0, 724, 840]
Region SurfaceDamageRegion (this=739b84edb088 count=1)
[ 0, 0, 0, 0]
layerStack= 0, z= 0, pos=(676,0), size=( 48, 840), crop=[ 0, 0, 48, 840], finalCrop=[ 0, 0, -1, -1], isOpaque=0, invalidate=0, dataspace=Default, defaultPixelFormat=RGBA_8888, color=(0.000,0.000,0.000,1.000), flags=0x00000000, tr=[1.00, 0.00][0.00, 1.00]
parent=90fc77d DockedStackDivider#0assign ``
zOrderRelativeOf=none
activeBuffer=[ 48x 840: 48,RGBA_8888], queued-frames=0, mRefreshPending=0, windowType=2034, appId=10032
The BufferLayer (splitScreenDividerAnchor#0) is the SplitScreenDividerAnchor, and it is the parent of DockedStackDivider.
Show/Dismiss
In WindowManagerService.performLayout, it will send message with id UPDATE_DOCKED_STACK_DIVIDER to DockedStackDividerController.reevaluateVisibility to notify the divider visibility. The DockedStackDividerController uses the listener IDockedStackListener to notify Divider in systemui.
Divier.updateVisibility
if (mVisible != visible) {
mVisible = visible;
mView.setVisibility(visible ? View.VISIBLE : View.INVISIBLE);
// Update state because animations won't finish.
mView.setMinimizedDockStack(mMinimized, mHomeStackResizable);
}
The mView is DividerView. So there is a new conclusion: when the system enters split screen mode, it will trigger Divider in systemui to show divider window with type TYPE_DOCK_DIVIDER; otherwise it will trigger Divider to dismiss divider window.
Resize
When we drag the divider for split screen windows, the system will change the split screen windows size. The process of dragging is done by DividerView in system ui.
DividerView.getFlingAnimator
anim.addUpdateListener(animation -> resizeStackDelayed((int) animation.getAnimatedValue(),
taskPositionSameAtEnd && animation.getAnimatedFraction() == 1f
? TASK_POSITION_SAME
: snapTarget.taskPosition,
snapTarget));
DividerView.resizeStack
mWindowManagerProxy.resizeDockedStack(/* different input parameters*/);
When dragging divider, the DividerView will call WindowManagerProxy.resizeDockedStack to resize dock stacks or split screen stacks. The final worker for resizing docked stack is ActivityManagerService.resizeDockedStackLocked. It will resize split screen primary stack, and resize other split screen secondary stacks to the left bounds of screen with ActivityManagerService.resizeStackLocked. So the resizing of docked stack only focused on split screen primary stack, and split screen secondary will change based on the split screen primary stack size.
If we drag divider to the left edge or right edge of screen, the DividerView will dismiss split screen primary stack or maximize split screen primary stack.
DividerView.commitSnapFlags
private void commitSnapFlags(SnapTarget target) {
if (target.flag == SnapTarget.FLAG_NONE) {
return;
}
boolean dismissOrMaximize;
if (target.flag == SnapTarget.FLAG_DISMISS_START) {
dismissOrMaximize = mDockSide == WindowManager.DOCKED_LEFT
|| mDockSide == WindowManager.DOCKED_TOP;
} else {
dismissOrMaximize = mDockSide == WindowManager.DOCKED_RIGHT
|| mDockSide == WindowManager.DOCKED_BOTTOM;
}
if (dismissOrMaximize) {
mWindowManagerProxy.dismissDockedStack();
} else {
mWindowManagerProxy.maximizeDockedStack();
}
mWindowManagerProxy.setResizeDimLayer(false, WINDOWING_MODE_UNDEFINED, 0f);
}
Whether dismiss/maximize split screen primary stack, the WindowManagerProxy will invoke ActivityManagerService.dismissSplitScreenMode to handle the request. The ActivityManagerService.dismissSplitScreenMode just sets the split screen stack windowing mode to WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN by invoking ActivityStack.setWindowingMode. From the above analyzing, we know if there is split screen primary stack, the ActivityDisplay.resolveWindowingMode will change windowing mode WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN to WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY. In ActivityStack.setWindowingMode, there is a rigid but useful logic to handle it:
ActivityStack.setWindowingMode
if (splitScreenStack == this && windowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY) {
// Resolution to split-screen secondary for the primary split-screen stack means we want
// to go fullscreen.
windowingMode = WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN;
}
It will change the split screen primary stack windowing mode to WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN, although the ActivityDisplay.resolveWindowingMode changes it to WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY, when ActivityManagerService wants to dismiss split screen mode. What’s a fucking but useful logic.
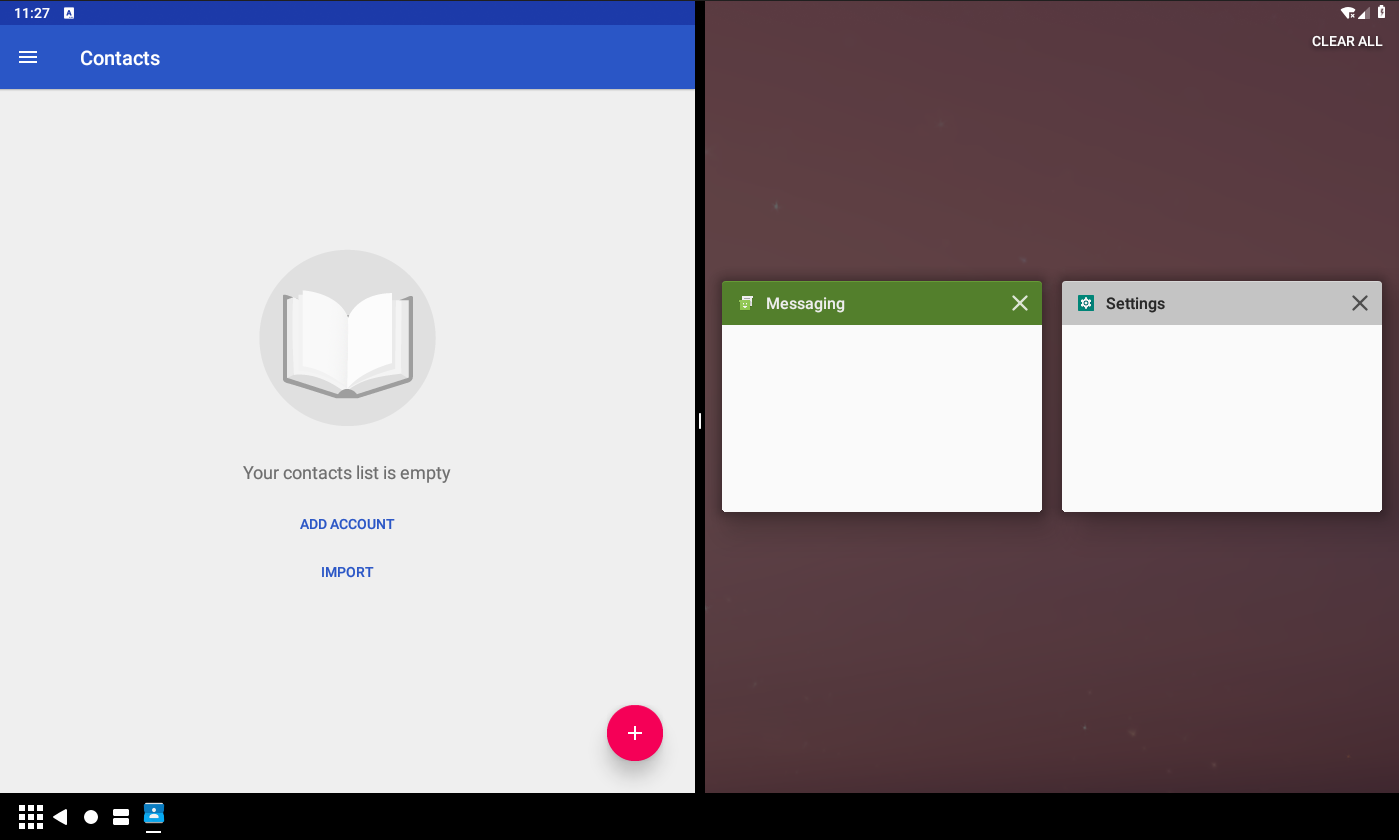
Click home button when system is in split screen mode
If we click the home button when the system is in split screen mode, the system will looks like following screenshot:
Clicking home button will start launcher to front, and then WindowManagerService.performSurfacePlacement will trigger DockedStackDividerController.checkMinimizeChanged.
DockedStackDividerController.checkMinimizeChanged
final TaskStack topSecondaryStack = mDisplayContent.getTopStackInWindowingMode(
WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY);
final RecentsAnimationController recentsAnim = mService.getRecentsAnimationController();
final boolean minimizedForRecentsAnimation = recentsAnim != null &&
recentsAnim.isSplitScreenMinimized();
boolean homeVisible = homeTask.getTopVisibleAppToken() != null;
if (homeVisible && topSecondaryStack != null) {
// Home should only be considered visible if it is greater or equal to the top secondary
// stack in terms of z-order.
homeVisible = homeStack.compareTo(topSecondaryStack) >= 0;
}
setMinimizedDockedStack(homeVisible || minimizedForRecentsAnimation, animate);
If home stack is visible, and its stack is on the top of top split screen secondary stack, the DockedStackDividerController.checkMinimizeChanged will call DockedStackDividerController.setMinimizedDockedStack to set minimized docked state.
DockedStackDividerController.setMinimizedDockedStack
if (isHomeStackResizable()) {
notifyDockedStackMinimizedChanged(minimizedDock, animate,
true /* isHomeStackResizable */);
minimizedChange = true;
}
If home stack is resizable, it will call DockedStackDividerController.notifyDockedStackMinimizedChanged to notify Divider minimized docked state based on IDockedStackListener.
In DividerView.setMinimizedDockStack, it will set the divider window position to mMinimizedSnapAlgorithm.getMiddleTarget().position if the minimized state is true:
DividerView.setMinimizedDockStack
stopDragging(minimized
? mSnapTargetBeforeMinimized.position
: getCurrentPosition(),
minimized
? mMinimizedSnapAlgorithm.getMiddleTarget()
: mSnapTargetBeforeMinimized,
animDuration, Interpolators.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN, 0);
The mMinimizedSnapAlgorithm.getMiddleTarget() is added by DividerSnapAlgorithm.addMinimizedTarget:
private void addMinimizedTarget(boolean isHorizontalDivision, int dockedSide) {
// In portrait offset the position by the statusbar height, in landscape add the statusbar
// height as well to match portrait offset
int position = mTaskHeightInMinimizedMode + mInsets.top;
if (!isHorizontalDivision) {
if (dockedSide == DOCKED_LEFT) {
position += mInsets.left;
} else if (dockedSide == DOCKED_RIGHT) {
position = mDisplayWidth - position - mInsets.right - mDividerSize;
}
}
mTargets.add(new SnapTarget(position, position, SnapTarget.FLAG_NONE));
}
In our landscape occasion, the position is mTaskHeightInMinimizedMode + mInsets.top, and the mTaskHeightInMinimizedMode is read from resource:
DividerSnapAlgorithm.DividerSnapAlgorithm
mTaskHeightInMinimizedMode = res.getDimensionPixelSize(
com.android.internal.R.dimen.task_height_of_minimized_mode);
So the DividerView will resize split screen primary width to mTaskHeightInMinimizedMode + mInsets.top, and we can change com.android.internal.R.dimen.task_height_of_minimized_mode to change its default size.
Click recents button when system is in split screen mode
If we click the recents button when the system is in split screen mode with minimized state, the state after clicking home button, the system will looks like following screenshot:
The calling chain is the same as clicking home button when system is in split screen mode, but with the false value for minimized state. From the DividerView.setMinimizedDockStack, we know if the minimized is false, the position will be mSnapTargetBeforeMinimized.position:
DividerView.setMinimizedDockStack
stopDragging(minimized
? mSnapTargetBeforeMinimized.position
: getCurrentPosition(),
minimized
? mMinimizedSnapAlgorithm.getMiddleTarget()
: mSnapTargetBeforeMinimized,
animDuration, Interpolators.FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN, 0);
In DividerView.injectDependencies, we know mSnapTargetBeforeMinimized = mSnapAlgorithm.getMiddleTarget(). So if we click recents button after clicking home buffer when system is in split screen mode, the divider window will be the middle of screen.
Recents button changing
NavigationBarView.onFinishInflate will register its docked listener to DockedStackExistsListener.
NavigationBarView.onFinishInflate
DockedStackExistsListener.register(mDockedListener);
And DockedStackExistsListener will register itself to WindowManagerService to receive docked stack state event.
DockedStackExistsListener
static {
try {
WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowManagerService().registerDockedStackListener(
new IDockedStackListener.Stub() {
// Other code
@Override
public void onDockedStackExistsChanged(boolean exists)
throws RemoteException {
DockedStackExistsListener.onDockedStackExistsChanged(exists);
}
// Other code
});
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed registering docked stack exists listener", e);
}
}
We have seen IDockedStackListener before, and it will be called in DockedStackDividerController.notifyDockedStackExistsChanged.
When docked stack existing state changed, NavigationBarView.updateRecentsIcon will be called to update recents button icon. The icon for docked stack existing state is retrieved by code mDockedIcon = getDrawable(lightContext, darkContext, R.drawable.ic_sysbar_docked). So if we want to change default docked icon of recents button, we can change the ic_sysbar_docked.
Bring home stack to front
If we start app from recents, the system will try to move home stack to front.
ActivityStack.moveToFront
if (!isActivityTypeHome() && returnsToHomeStack()) {
// Make sure the home stack is behind this stack since that is where we should return to
// when this stack is no longer visible.
mStackSupervisor.moveHomeStackToFront(reason + " returnToHome");
}
ActivityStackSupervisor.findTaskToMoveToFront
if ((flags & ActivityManager.MOVE_TASK_WITH_HOME) != 0
|| (prev != null && prev.isActivityTypeRecents())) {
// Caller wants the home activity moved with it or the previous task is recents in which
// case we always return home from the task we are moving to the front.
moveHomeStackToFront("findTaskToMoveToFront");
}
ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityFromRecents
if (windowingMode != WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARY) {
// We always want to return to the home activity instead of the recents activity
// from whatever is started from the recents activity, so move the home stack
// forward.
moveHomeStackToFront("startActivityFromRecents");
}
There are three occasion to bring home stack to front when starting app from recents:
- If we move one stack to front, and it is not home type, and it wants to return to home stack. When we starts recents, the system will move recents stack to front. Because the recents has the type recents, and it will pass the
ActivityStack.returnsToHomeStackchecking, so the recents will bring home stack to front. If there are many visible freeform windows before starting recents, other freeform windows will be invisible if we start one freeform window from recents, because home stack is over other freeform window stacks. - If previous task is recents type, the
ActivityStackSupervisor.findTaskToMoveFrontwill bring home stack to front. - If we start an app from recents with non-
WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARYwindowing mode, theActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityFrontRecentswill bring home stack to front.
Summary
The recents is the entry for split screen. When we select on app to start on split screen, the recents will bind windowing mode WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARY and task id for it. The system will try to restore task from /data/system_ce/user_id/recents_task/*_task.xml.
If the windowing mode is WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_PRIMARY, the system will change other stacks in the same display to WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY. The system will notify the Divider in system ui to show divider window when system enters split screen mode.
If we drag divider window, the DividerView in system ui will call ActivityManagerService to resize split screen primary stack, and based on its size to resize split screen secondary stacks in the same display.
If we drag divider window the left/right edge of screen, the DividerView in system ui will call ActivityManagerService to dismiss split screen mode, and change split screen primary stack windowing mode WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN.
If system is in split screen mode, and we start an app with windowing mode WINDOWING_MODE_FULLSCREEN, the ActivityDisplay.resolveWindowingMode will change windowing mode to WINDOWING_MODE_SPLIT_SCREEN_SECONDARY.
The divider window uses the specific type TYPE_DOCK_DIVIDER. And DisplayContent.AboveAppWindowContainers uses a specific surface called SplitScreenDividerAnchor as the parent of divider window.