Analyze picture in picture
This article based on
AOSP9.0.
PIP is another multi-window feature I used very much when watching videos. This article will analyze its logic to show its details.
Enter picture-in-picture(pip)
We can enter pip by API Activity.enterPictureInPictureMode. If the activity supports pip, it will call ActivityManagerService.enterPictureInPictureMode to do the real work.
ActivityManagerService.enterPictureInPictureMode
// Adjust the source bounds by the insets for the transition down
final Rect sourceBounds = new Rect(r.pictureInPictureArgs.getSourceRectHint());
mStackSupervisor.moveActivityToPinnedStackLocked(r, sourceBounds, aspectRatio,
"enterPictureInPictureMode");
final PinnedActivityStack stack = r.getStack();
stack.setPictureInPictureAspectRatio(aspectRatio);
stack.setPictureInPictureActions(actions);
The ActivityManagerService.enterPictureInPictureMode will move activity to pinned stack, and then update PinnedActivityStack states. The PinnedActivityStack is the implementation of ActivityStack, and will process specific logic for pip.
ActivityStackSupervisor.moveActivityToPinnedStackLocked
PinnedActivityStack stack = display.getPinnedStack();
if (stack != null) {
moveTasksToFullscreenStackLocked(stack, !ON_TOP);
}
// Other code
resizeStackLocked(stack, task.getOverrideBounds(), null /* tempTaskBounds */,
null /* tempTaskInsetBounds */, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS,
true /* allowResizeInDockedMode */, !DEFER_RESUME);
if (task.mActivities.size() == 1) {
task.reparent(stack, ON_TOP, REPARENT_MOVE_STACK_TO_FRONT, !ANIMATE, DEFER_RESUME,
false /* schedulePictureInPictureModeChange */, reason);
} else {
final TaskRecord newTask = task.getStack().createTaskRecord(
getNextTaskIdForUserLocked(r.userId), r.info, r.intent, null, null, true);
r.reparent(newTask, MAX_VALUE, "moveActivityToStack");
newTask.reparent(stack, ON_TOP, REPARENT_MOVE_STACK_TO_FRONT, !ANIMATE,
DEFER_RESUME, false /* schedulePictureInPictureModeChange */, reason);
}
The ActivityStackSupervisor.moveActivityToPinnedStackLocked will move all tasks in pinned stack to fullscreen, and resize pinned stack to the assigned bounds. It also reparents task of activity to the pinned stack. If origin task has multiple activities, it will move top activity to pinned stack, and keep other activities in origin task.
The following screenshot is an example:
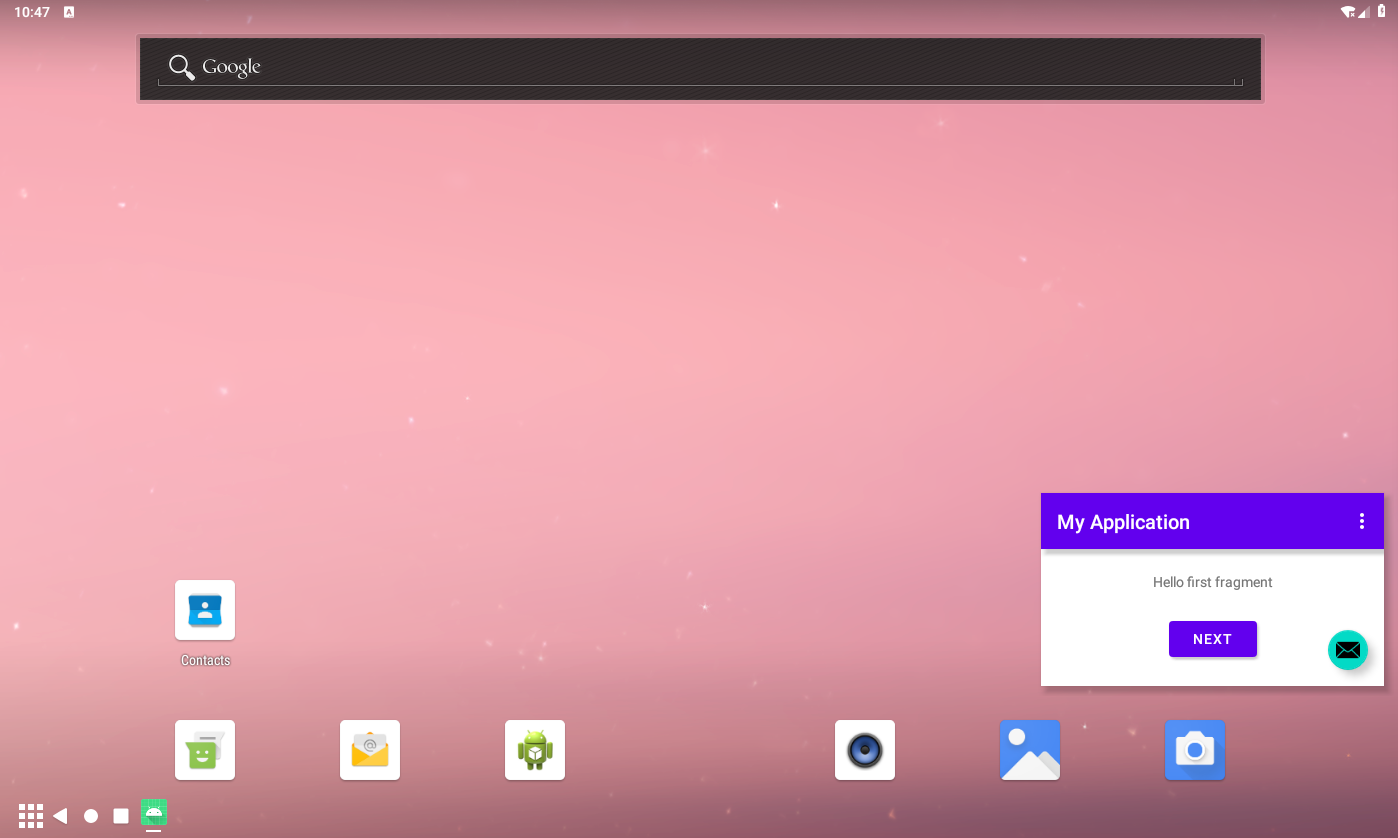
Input
In system ui, there is a system ui service called PipUI to process the ui of pip. The PipUI is entry for PipManager to receive command from frameworks.
Pip input consumer
The PipManager will create an instance of InputConsumerController called mInputConsumerController, to manage pip input consumer to receive the input from input flinger with its registerInputConsumer.
PipManager.initialize
mInputConsumerController = InputConsumerController.getPipInputConsumer();
mInputConsumerController.registerInputConsumer();
InputConsumerController.registerInputConsumer
final InputChannel inputChannel = new InputChannel();
try {
mWindowManager.destroyInputConsumer(mName);
mWindowManager.createInputConsumer(mToken, mName, inputChannel);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to create input consumer", e);
}
mInputEventReceiver = new InputEventReceiver(inputChannel, Looper.myLooper());
if (mRegistrationListener != null) {
mRegistrationListener.onRegistrationChanged(true /* isRegistered */);
}
In InputMonitor.accept, it will use pip stack bounds to restrict pip input consumer touchable region:
InputMonitor.accept
if (w.inPinnedWindowingMode()) {
if (mAddPipInputConsumerHandle
&& (inputWindowHandle.layer <= pipInputConsumer.mWindowHandle.layer)) {
// Update the bounds of the Pip input consumer to match the window bounds.
w.getBounds(mTmpRect);
pipInputConsumer.mWindowHandle.touchableRegion.set(mTmpRect);
addInputWindowHandle(pipInputConsumer.mWindowHandle);
mAddPipInputConsumerHandle = false;
}
// Other code
}
The pip consumer has the fixed name called pip_input_consumer, so InputMonitor can retrieve pip consumer by name.
The InputMonitor.createInputConsumer will set FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL to pip window handle layout params flags to ensure other events fall through, and pip input consumer target consumes all events for pip/pinned stack.
InputMonitor.createInputConsumer
case INPUT_CONSUMER_PIP:
// The touchable region of the Pip input window is cropped to the bounds of the
// stack, and we need FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL to ensure other events fall through
consumer.mWindowHandle.layoutParamsFlags |= FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
break;
When InputConsumerController.InputEventReceiver receives the input events from input flinger, it will call InputConsumerController.TouchListener to notify the input events, that set by inputConsumerController.setRegistrationListener in PipTouchHandler.PipTouchHandler.
If we click the pip window as normal, it will show pip menu by starting PipMenuActivity over the pip window, looks like following screenshot:
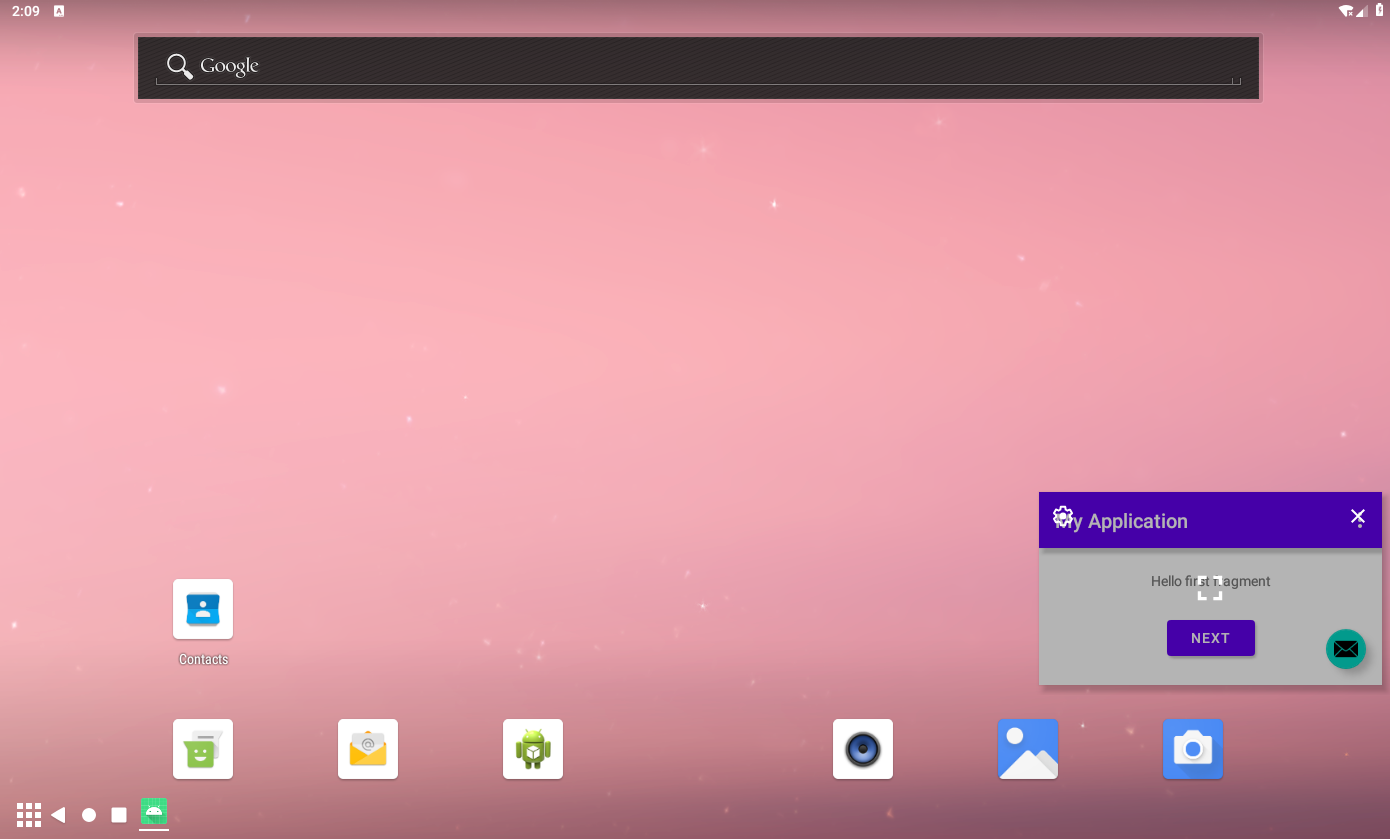
If we do nothing after showing pip menu some time, it will dismiss the pip menu.
If we double tap the pip window, it will dismiss pip, and move tasks in pip/pinned stack to fullscreen stack by calling ActivityManagerService.dismissPip:
ActivityManagerService.dismissPip
if (animate) {
stack.animateResizePinnedStack(null /* sourceHintBounds */,
null /* destBounds */, animationDuration, false /* fromFullscreen */);
} else {
mStackSupervisor.moveTasksToFullscreenStackLocked(stack, true /* onTop */);
}
KEYCODE_WINDOW
For key event, in PhoneWindowManager.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing, it will response to KEYCODE_WINDOW to show pip menu when pip is visible by PhoneWindowManager.showPictureInPictureMenu. And PipManager.showPictureInPictureMenu will process it.
Focusable
In WindowConfiguration.canReceiveKeys, it will not allow pip/pinned stack to receive keys:
WindowConfiguration
public boolean canReceiveKeys() {
return mWindowingMode != WINDOWING_MODE_PINNED;
}
And this method will be used to check whether one ConfigurationContainer is focusable.
ActivityStackSupervisor.isFocusable
return container.getWindowConfiguration().canReceiveKeys() || alwaysFocusable;
AppWindowToken
boolean windowsAreFocusable() {
return getWindowConfiguration().canReceiveKeys() || mAlwaysFocusable;
}
So if the pip/pinned window doesn’t set it always focusable(set FLAG_ALWAYS_FOCUSABLE), it is not focusable.
Always on top
In WindowConfiguration.isAlwaysOnTop, it will set pip/pinned stack always on top.
WindowConfiguration
public boolean isAlwaysOnTop() {
return mWindowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_PINNED;
}
For example, in DisplayContent.positionChildAt, it will set pip/pinned stack to the top over other stacks in this display:
DisplayContent.positionChildAt
if (child.getWindowConfiguration().isAlwaysOnTop()
&& position != POSITION_TOP) {
// This stack is always-on-top, override the default behavior.
Slog.w(TAG_WM, "Ignoring move of always-on-top stack=" + this + " to bottom");
// Moving to its current position, as we must call super but we don't want to
// perform any meaningful action.
final int currentPosition = mChildren.indexOf(child);
super.positionChildAt(currentPosition, child, false /* includingParents */);
return;
}
Receive pip stack event from ActivityManagerService
In PipManager, there is an TaskStackChangeListener implementation called mTaskStackListener. In PipManager.initialize, it will register mTaskStackListener to ActivityManagerService to receive pip stack event.
PipManager.initialize
ActivityManagerWrapper.getInstance().registerTaskStackListener(mTaskStackListener);
Summary
The Activity.enterPictureInPictureMode will notify ActivityManagerService to move activity to pinned stack. If there are tasks in pinned stack, the AMS will move existing tasks to fullscreen stack. If the task of activity exists has multiple activities, it will keep other activities to origin task, and create new task for pip/pinned activity.
The pip/pinned window can’t receive keys, and system ui will create pip input consumer to receive input for pip/pinned stack. When input event received, pip ui will show PipMenuActivity to display pip menu. If we double tap the pip/pinned window, it will dismiss pip and move tasks in pip stack to fullscreen stack through ActivityManagerService.
The pip ui also uses TaskStackChangeListener to receive pip event from ActivityManagerService.